IHACC PhD student Melanie Flynn recently published an article in Environmental Science & Policy. Melanie conducted a systematic review of the literature to identify and evaluate how participatory scenario planning has been used in the Arctic. Congrats Mel!
CITATION: Flynn, M., Ford, J., Pearce, T., and Harper, S.L. (2018). Participatory scenario planning and climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability research in the Arctic. Environmental Science & Policy. 79:45–53.
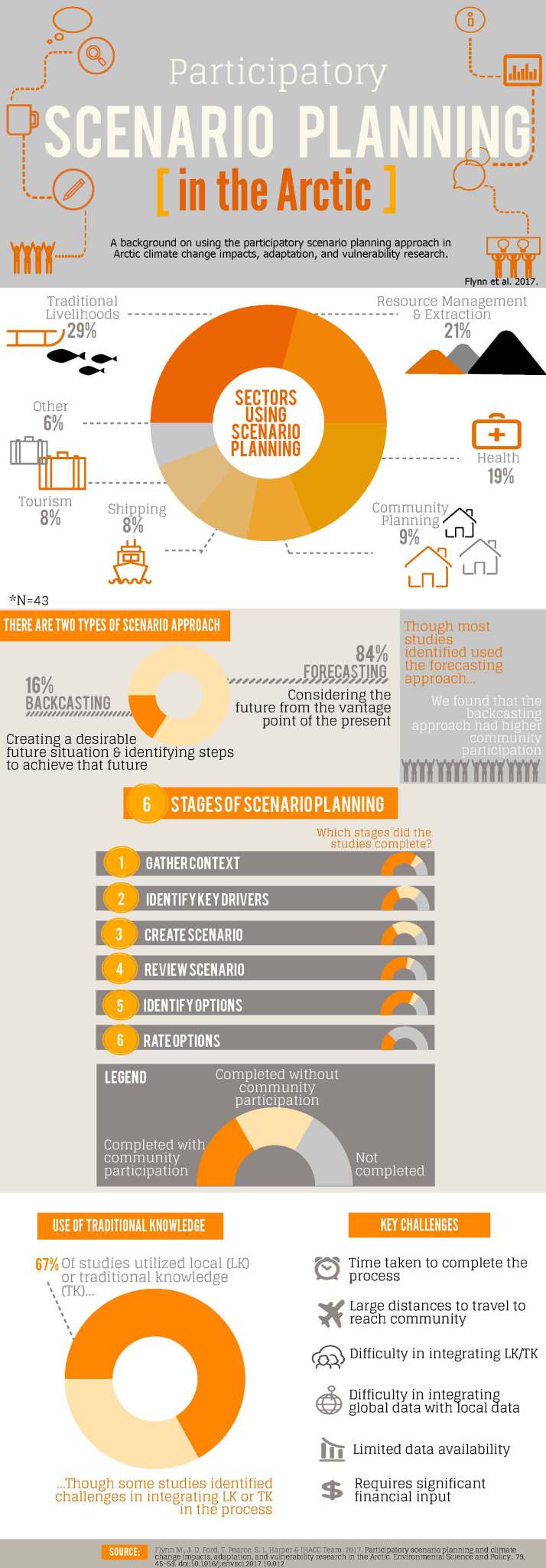
ABSTRACT: Participatory scenario planning (PSP) approaches are increasingly being used in research on climate change impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability (IAV). We identify and evaluate how PSP has been used in IAV studies in the Arctic, reviewing work published in the peer-reviewed and grey literature (n = 43). Studies utilizing PSP commonly follow the stages recognized as ‘best practice’ in the general literature in scenario planning, engaging with multiple ways of knowing including western science and traditional knowledge, and are employed in a diversity of sectors. Community participation, however, varies between studies, and climate projections are only utilized in just over half of the studies reviewed, raising concern that important future drivers of change are not fully captured. The time required to conduct PSP, involving extensive community engagement, was consistently reported as a challenge, and for application in Indigenous communities requires careful consideration of local culture, values, and belief systems on what it means to prepare for future climate impacts.



 Dr. James Ford
Dr. James Ford Dr. Sherilee Harper
Dr. Sherilee Harper Anna Bunce
Anna Bunce Kaitlyn Finner
Kaitlyn Finner Knut Tjensvoll Kitching
Knut Tjensvoll Kitching Carlee Wright
Carlee Wright Manpreet Saini
Manpreet Saini






